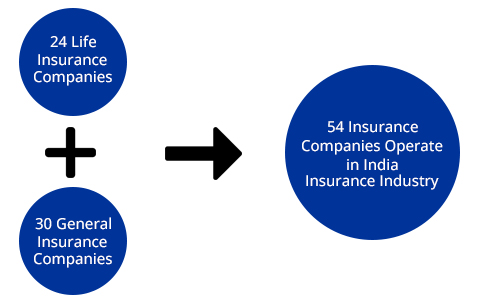
Indian Insurance Industry comprises 54 Insurance Companies out of which 24 insurers are in the Life Insurance business offering life products. And 30 insurers are in the General Insurance business providing non-life/general insurance products to the customers countrywide.
Life Insurance Corporation of India (LIC) is the market leader in the life insurance industry in India. With the entry of private players coupled with international expertise. The Indian insurance market has a wider potential to tap.
Insurance service is one of the oldest services, serving mankind approx. 200 years. In few areas of world and Insurance is also one of the best ways to earn money from old days. Both things are the same from different perspectives and we all agree on one thing everyone deserves a reward for his service. The way insurance service becomes a worldwide source of income is incredible. And it gives a brief idea about the insurance service and the demand between people.
Table Content
History of the Indian Insurance Industry
From the historical perspective, Insurance finds are mentioned in Manusmrithi, Arthasastra, and Dharmasastra. The accumulation of resources that can be re-distributed at times of calamities like floods, fire, famine, etc. This was just like a portent to present-day insurance. The insurance market in India has grown over time.
Let’s talk about rising of Indian Insurance Industry. And try to take look at their struggle in the market as a new product. Currently, 54 Insurance Companies are running in India with the permission of IRDAI. Among all these companies some companies are joint ventures of two different companies. Some different companies belong from different countries and they have a rich history. Most Indian Insurance Industries come to the Indian market in early 2000 between 2008 and they are doing some of the best jobs till today.
Life Insurance Business
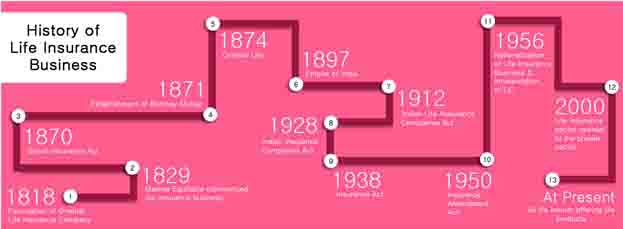
The British Insurance Act was enacted in the year 1870 and after that, the Bombay Mutual in the year 1871. Oriental in the year 1874 and Empire of India in the year 1897 started the insurance business in the Bombay Residency. There were several foreign insurance companies such as Albert Life Assurance, London Globe Insurance, and Royal Insurance. And the Indian insurance companies were receiving harsh competition from their foreign counterparts.
It was the year 1912 when Insurance regulation was firstly implemented in India by The Indian Life Assurance Companies Act, 1912. The Indian Insurance Companies Act was enacted in 1928 which was aimed to facilitate the government in a way towards collecting statistical information for both the life and non-life business conducted in India.
To secure the interests of the insurance buyers, the former legislation was amended by the Insurance Act, 1938 which ensures an efficient mechanism to control over insurance business. The Insurance Amendment Act, of 1950 eliminated Principal Agencies. Still, there were a large number of insurance companies, and there were accusations of unfair business practices.
The Government then decided to nationalize the insurance business. On 19th January 1956, the Life Insurance sector was nationalized, and the Life Insurance Corporation of India (LIC) was established on 1st September 1956. LIC enjoyed a monopoly till the year 2000 when the Insurance sector was opened to the private sector.
General Insurance Business
General Insurance in India was commenced with the establishment of Triton Insurance Company Ltd. in Kolkata during the year 1850. The Indian Mercantile Insurance Ltd. was founded in the year 1907 and conducted all categories of general insurance business.
General Insurance Council was formed in 1957, which crafted a code of conduct for ensuring fair and sound business practices. Thereafter, the Insurance Act was amended in 1968 with an aim to control investments and set minimum solvency margins.
In the year 1972, the General Insurance Business (Nationalization) Act was passed that led to the nationalization of the general insurance business on 1st January 1973. With the amalgamation of 107 insurance companies, four insurers namely National Insurance Company, Oriental Insurance Company, United India Insurance Company, and New India Assurance Company were established. The General Insurance Corporation of India was incorporated in 1971, and it commenced its business on 1st January 1973.
The scenario of the Indian Insurance Industry
Globally, the share of the life insurance business regarding premiums is 55.6%, and the proportion of the non-life insurance premium is 44.4 %. India contributes 0.75% to the global non-life premium and 2.24% to the global life insurance market. In India, the share of the life insurance business stands at 79% and the non-life insurance business has 21% of the market share during the year 2015.
India is ranked 10th among 88 countries for life insurance business and 18th among 88 countries for non-life insurance business. In 2015, the life insurance premium increased by 7.8% and the non-life insurance premium increased by 8.1%.
When it comes to the insurance business in India, the Insurance Regulatory and Development Authority of India (IRDAI) was established as a statutory body in April 2000. Its key objectives include the protection of the interests of policyholders along with the promotion of competition that enhances customer satisfaction while ensuring the financial security of the insurance market.
Insurance Penetration & Density in India
Insurance penetration and density signify the development of the insurance sector in a country. Insurance penetration is expressed as a percentage of premium to GDP and Insurance density is expressed as a ratio of premium to the population.
During the first-decade post liberalization in the insurance sector, the insurance penetration increased from 2.71% in the year 2001 to 5.20% in the year 2009. In the year 2014, it was 3.3%, and in 2015, it was 3.44%. The insurance density increased from US$ 11.5 in the year 2001 to US$ 64.4 in the year 2010. In the year 2015, it was US$ 54.7.
For the Life Insurance business, the insurance penetration increased from 2.15% in the year 2001 to 4.60% in the year 2009. In the year 2014, it was 2.6%, and in 2015, it was 2.72%. The insurance density increased from US$ 9.1 in the year 2001 to US$ 55.7 in the year 2010. In the year 2015, it was US$ 43.2.
For the Non-Life Insurance business, the insurance penetration remained stable within the range of 0.5%-0.8%. The insurance density increased from US$ 2.4 in the year 2001 to US$ 11.5 in the year 2015.
Life Insurance Premium Income, Indian Insurance Industry
The Life Insurance sector in India recorded a premium income of Rs 366943.23 crores during 2015-16 with a growth rate of 11.84%. LIC recorded 11.17% growth, and private insurers registered 13.64% growth in premium income. During 2015-16, the life insurance business registered a growth of 6.20% in renewal premium and 22.53% in the first-year premium.
Considering the total premium received, LIC decreased its market share to 72.61% during 2015-16 compared to 73.05% in 2014-15. Private insurers registered an increase in the market share and stood at 27.39% in 2015-16.
The total capital of the life insurers as of 31st March 2016 stood at Rs 26,691.47 crores. In 2015-16, private sector insurers brought an additional capital of Rs 451.91 crores to the industry.
General/Non-Life Insurance Premium Income
The non-Life Insurance industry received a total direct premium of Rs 96,379 crore in India with a growth rate of 13.81% during the year 2015-16. In the same year, the public sector insurers achieved a growth rate of 12.08%, whereas private general insurers registered a growth rate of 13.12%.
In the year 2015-16, the standalone health insurers achieved a growth rate of 41.12%, and the specialized insurers registered a growth rate of 18.04%.
The total paid-up capital till 31st March 2015 was Rs 11,504 crores. During 2015-16, non-life insurers infused Rs 1099 crores. The total paid-up capital for non-life insurers in the year 2015-16 was Rs 12,603 crores.
(Note: facts & figures mentioned above are as per IRDAI annual report 2015-16)
Future Ahead
The insurable population in India is estimated to touch around 750 million by the year 2020. The Insurance market in India is anticipated to quadruple in size over the next ten years. And the life insurance market is expected to cross US$ 160 billion. General Insurance in India is projected to grow at a rate of 17%.
Life Insurance in India is expected to comprise 35% of the total savings. The life insurance industry looks quite promising, considering several regulatory changes. That will modify the way industry offers life products & engage proactively with its customers.
Demographic factors such as increasing household incomes, young insurable population, liberal policies, growing technology, etc. lead to tremendous business opportunities yet to be harnessed.
(Source: IBEF.org)
The Insurance market in India can be traced back to the 19th century, and there have been major transformations in the industry that ensures fair business practices. The incorporation of IRDAI (Indian Insurance Regulator) has put forth several regulatory changes.
At present, India accounts for less than 1.5% of the world’s total insurance premiums, despite being the second-most populous nation. The Indian Insurance market has immense potential to grow exponentially in the forthcoming years.